

If an appropriate modification is employed to the electrospinning, it can prepare nanofibers with some specific secondary structure. Nanofibers which be prepared by electrospinning, usually exhibit a solid interior and smooth surface. In theory, electrospinning can be applied to all polymer to get nanofibers. It makes the process particularly suitable for the production of fibres using macromolecule or polymer. The spinning fibers process is non-invasive and does not require the use of coagulation invasion to produce solid threads from liquid. The common setup and working principle of electrospinning.Įlectrospinning shares characteristics of both electrospraying and conventional solution dry spinning of fibers. In this process, the ultrathin fibers solidify or dry rapidly, and then the nanofibers are collected on the “Collector”. Due to the electrostatic repulsion of the charges in the polymer liquid, the polymer liquid is drawn thinner and thinner, as the fiber spin part in Figure 1. Under pulling of electrostatic force, polymer liquid is drawn and got a “Taylor cone” at the jut of spinneret, then is drawn out from spinneret as the “Liquid jet” part in Figure 1. A high voltage and a cuspidate spinneret provided by a point electrode creates a charge aggregation into the polymer solution or liquid at the spinneret of syringe. Figure 1 shows the common setup and working principle of electrospinning. It uses an electrical charge to draw a very fine (typically on the micro or nano scale) fibers from liquid. Furthermore, we will introduce some encapsulation of stimulating responsive materials into core-shell nanofibers, and the improvement of the responsibility and functional devices applications for the combination of core-shell nanofibers and stimulating responsive materials.Įlectrospinning, also known as electrostatic spinning, has been developed since 1990s as micro-nano fiber and particle fabrication technique ( Reneker et al, 1996 Huang et al, 2003). Here, based on complex electrospinning technique, we will describe nanofibers with nano-channel and core-shell nano-capsule fabrication, and how coaxial electrospinning is working to construct various nanostructures in the nanofibers. Coaxial electrospinning is an effective, fast and controlled technique to construct core-shell nanostructures into nanofibers ( Li et al, 2004 Zhang et al., 2004 and Xia et al., 2006).
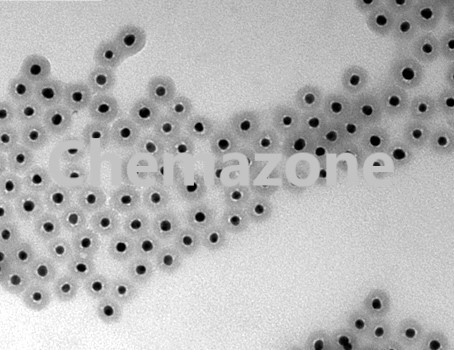
Especially, core-shell nanofibers pull more and more interesting and attention, because of the great potential applications and prospects for nanochannel, nanocapsule and small encapsulating devices. Various nanofibers with different secondary nanostructure were fabricated. Utilizing electrostatic interactions and through the elongation of viscoelastic jet device, electrospinning technique can copy the structure of jet device to nanoscale fibers from polymer solution or molten.

Following the fast and polymer common property, scientists invented complex electrospinning. In lots of synthetic and fabrication methods, electrospinning (a drawing process based on electrostatic interactions) provided the simplest approach to nanofibers with exceptionally long in length, uniform in shape, and diversified in composition ( Li et al., 2004 Greiner et al., 2007). Nanofibers, one-dimensional (1D) nanostructures have been paid great attentions due to their unique properties and intriguing applications in many areas (Xia et al., 2003). In the last 30 years, nano science and technology have an unprecedented development.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
